striped bass
 Hack [hak] (n) – A clever trick, skill, or shortcut to increase productivity and efficiency.
Hack [hak] (n) – A clever trick, skill, or shortcut to increase productivity and efficiency.
1. Find the bait first, then look nearby for the fish.
2. All things being equal, go with chartreuse.
3. Fish in areas where you can see the current moving.
4. The sneakier the angler, the bigger the fish.
5. Use dark colored lures in low light situations and rainy days.
6. Color contrasts attract fish. Read More!
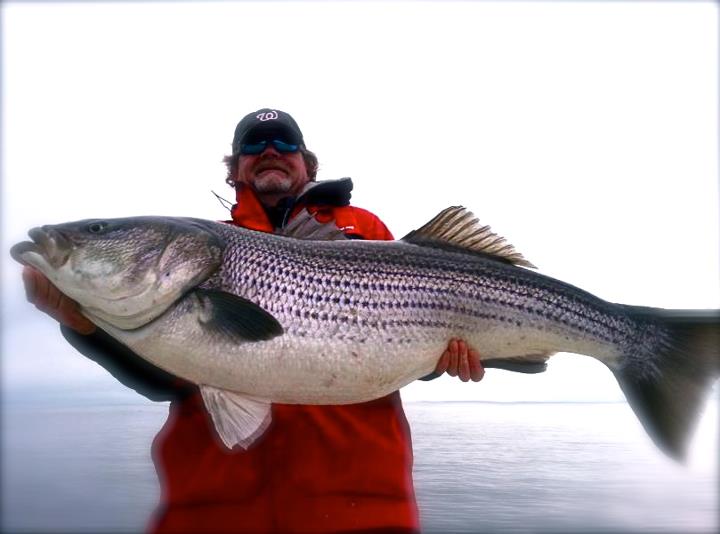
 Congratulations to Rich Jenkins, 2013 Champion of the Kent Narrows Light Tackle Catch-&-Release Tournament. Rich fished with Jamie Clough, Jon Griffiths and me onboard my 27 Judge CC Thunder Road and won the tournament with a wide-shouldered 34-inch striper caught about 1:00 PM Saturday afternoon. Coming off the win, I thought it might be helpful to post some recommendations for catching bigger striped bass in Maryland’s portion of the Chesapeake Bay in June.
Congratulations to Rich Jenkins, 2013 Champion of the Kent Narrows Light Tackle Catch-&-Release Tournament. Rich fished with Jamie Clough, Jon Griffiths and me onboard my 27 Judge CC Thunder Road and won the tournament with a wide-shouldered 34-inch striper caught about 1:00 PM Saturday afternoon. Coming off the win, I thought it might be helpful to post some recommendations for catching bigger striped bass in Maryland’s portion of the Chesapeake Bay in June.
Topwater – Look around high-current points where there is access to deep water. Submerged rocks and other cover are a plus. Set up downstream and fan-cast into the direction of the current starting closest to shore. Look for the rip, that is a change in the waves around the point and work that area hard. On calm days, use a spook. In rougher water, try a big popper. Heddon Super Spooks, Lonely Angler Zipsters, and Stillwater Smackits are great lures for this time of year. Read More!
 I’ve been lying low over the past couple of weeks waiting out the craziness. Most of my fishing has been in out-of-the-way places far from the madding crowds. Radios blaring, airplanes buzzing, stereos thumping, outboards droning, helicopters whirring, sirens wailing – Wow! Boat shows, trolling tournaments, and sailing regattas make the main stem of the Chesapeake very noisy. The Bay is fully awake from her winter slumber and the crowds are back in force. While we each enjoy the water in our preferred ways, to my thinking fishing should include elements of solitude and stealth. I’ve mentioned before that I’d rather pick up aluminum cans at rush hour along I-95 than try to pick off rockfish in the main channel on a busy trolling weekend. I prefer to look off the beaten path for places where I can tune-in to something a little more pleasing than the clamorous dissonance of the masses.
I’ve been lying low over the past couple of weeks waiting out the craziness. Most of my fishing has been in out-of-the-way places far from the madding crowds. Radios blaring, airplanes buzzing, stereos thumping, outboards droning, helicopters whirring, sirens wailing – Wow! Boat shows, trolling tournaments, and sailing regattas make the main stem of the Chesapeake very noisy. The Bay is fully awake from her winter slumber and the crowds are back in force. While we each enjoy the water in our preferred ways, to my thinking fishing should include elements of solitude and stealth. I’ve mentioned before that I’d rather pick up aluminum cans at rush hour along I-95 than try to pick off rockfish in the main channel on a busy trolling weekend. I prefer to look off the beaten path for places where I can tune-in to something a little more pleasing than the clamorous dissonance of the masses.
Since the striped bass spawn is winding down on the Chesapeake Bay, I thought it might be interesting to take a look at some post-spawn patterns. When stripers come off the spawning grounds, they’re usually hungry. If you can find them, they’re pretty easy to catch. Ah, but finding them, there’s the rub. Where should you look? Read More!
 UPDATE: This post originally appeared in March 2013. It has been updated due to recent proposals to require circle hooks year round for bait fishing in Maryland.
UPDATE: This post originally appeared in March 2013. It has been updated due to recent proposals to require circle hooks year round for bait fishing in Maryland.
It’s spring in the Chesapeake Bay and time for big migratory stripers. Some of the biggest striped bass in the world are caught in Maryland in the early spring. A few fishermen are already using circle hooks to catch & release big fish on the points near the rivers using bait such as bloodworms and cut menhaden. Circle hooks aren’t just a good idea for bait fishing in the Chesapeake Bay, they’re required by law. Maryland fishermen have been slow to see the advantages of circle hooks. I think that’s because most of us haven’t used them enough, but there’s also confusion about what circle hooks are and how they work. I recently had an opportunity to travel to Providence, Rhode Island to attend a FishSmart conference sponsored by NOAA about catch & release techniques. I came away with some interesting information.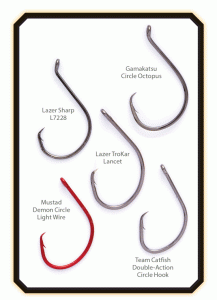
According to extension agents working with Florida Sea Grant, circle hooks have been used for decades in their state by both recreational and commercial fishermen who appreciate their ability to efficiently catch fish. The principle behind the hook is simple. After the hook has been swallowed, the fisherman applies pressure to the line, pulling the hook out of the stomach. The unique hook shape causes the hook to slide towards the point of resistance and embed itself in the jaw or in the corner of the fish’s mouth. The actual curved shape of the hook is intended to keep the hook from catching in the gut cavity or throat.
The advantage to the fisherman is that hooking is automatic. No hook set required. All we have to do is let the fish swim off with the bait then pick up the rod and start reeling. Circle hooks are a fool-proof way to catch stripers when fishing with bait, but do they work to protect the fish?
 According to Maryland rockfish scientist Rudy Lukacovic, most of the time they do. Most fishermen will tell you that they still see gut-hooked fish occasionally. That’s one of the drawbacks to bait fishing, but there’s also another problem. There is unfortunately no industry standard as to what makes a circle hook. In fact, some of the hooks you buy off the bait shop shelf may not be circle hooks at all. Just because it says circle hook on the package doesn’t mean it is. There are impostors.
According to Maryland rockfish scientist Rudy Lukacovic, most of the time they do. Most fishermen will tell you that they still see gut-hooked fish occasionally. That’s one of the drawbacks to bait fishing, but there’s also another problem. There is unfortunately no industry standard as to what makes a circle hook. In fact, some of the hooks you buy off the bait shop shelf may not be circle hooks at all. Just because it says circle hook on the package doesn’t mean it is. There are impostors.
On a true circle hook, the tip of the hook points back toward the shank of the hook. If it points toward the eye, it’s not a circle hook no matter what it says on the package. Confused? Then try this: Curve your index finger around the contour of the hook shank and press down a little. If you feel the tip of the hook pricking your finger, it’s not a true circle and won’t work right. The tip of the hook should curve away from your finger.
it says on the package. Confused? Then try this: Curve your index finger around the contour of the hook shank and press down a little. If you feel the tip of the hook pricking your finger, it’s not a true circle and won’t work right. The tip of the hook should curve away from your finger.
Circle hooks can be roughly divided into two types, offset and non-offset. The offset refers to the amount of deviation in the plane of the hook point relative to that of the shank. Most of the hooks you see on the store shelves are offset. That means when you lay them down on a table, they won’t lay completely flat. A true non-offset hook will lay perfectly flat on the table. Offset circle hooks are more likely to gut-hook your fish.
 Since there can be confusion about what constitutes a true circle hook, some tournaments are specifying certain brands and types as tournament legal. Unless the industry responds by standardizing descriptions, state resource departments and lawmakers may also have to be more specific. Maryland defines a circle hook as: A non-offset hook with the point turned perpendicularly back to the shank. Circle hooks used in bait fisheries should be “non offset”. That is, if the hook is laid on a flat surface, all parts of the hook lie flat on the surface.
Since there can be confusion about what constitutes a true circle hook, some tournaments are specifying certain brands and types as tournament legal. Unless the industry responds by standardizing descriptions, state resource departments and lawmakers may also have to be more specific. Maryland defines a circle hook as: A non-offset hook with the point turned perpendicularly back to the shank. Circle hooks used in bait fisheries should be “non offset”. That is, if the hook is laid on a flat surface, all parts of the hook lie flat on the surface.
Here are some tips for using circle hooks to catch striped bass:
Keep it limber – Use a slow, limber fishing rod with a lot of bend in the tip. A stiff, fast-tipped rod is more likely to pull the hook out of the striper’s mouth when you pick it up. Ugly Stix fans, this is your cue!
Don’t bury the hook in the bait – If you hide the hook, it is less likely to catch the corner of the fish’s mouth when you start reeling. If you use live bait, hook the bait through the nose or lips so the hook is completely exposed and the gap isn’t blocked. Stripers won’t see the hook and your bait will look more natural.
Crank, don’t yank – Just set your reel to free spool, wait for the fish to take off and start reeling. If you’re live-lining, count to ten before you start. Don’t set the hook.
No need to sharpen – Sharpening a circle hook will damage the tip and make less likely to hook the mouth but more likely to hook the fish’s stomach.
Stay away from stainless – If a fish breaks off, the stainless hooks don’t rust. That means it will stay in the fish’s mouth longer. If a fish swallows a stainless hook, it will probably die.
Go big or go home – Don’t be afraid to use a big hook. A 8/0 or 9/0 hook is great for stripers. Take a look at the big rockfish in the picture below. It takes a wide-gap hook to get over those thick lips! Hooks with a gap that are too small are more likely to gut-hook the fish. For big fish in the  spring, use 10/0 or even bigger. Also, pay attention to the quality of the hook because you don’t want a hook that will bend or straighten.
spring, use 10/0 or even bigger. Also, pay attention to the quality of the hook because you don’t want a hook that will bend or straighten.
Catch & Release Tips
Be Prepared – If you aren’t used to using circle hooks, it might take a little longer to remove the hook from your fish. Keep your pliers, de-hooker, measuring device, and camera beside you and ready to use. If the fish swallows the hook, just cut the line as close as you can to the hook. Don’t try to pull the hook out if it’s embedded in the fish’s stomach.
Do you really need a net? – It’s a lot easier just to reach down and lip the fish with wet hands or wet rubber coated gloves. Nets cause you to lose fish and they injure them by removing slime. If you must use one, find one that has a fine, rubber coated mesh. You might even consider a a cradle net since that will let you measure your fish in the water.
Handle With Care – If you plan to release a big fish, be sure to support the body weight with both hands. If you have to lay it down to remove the hook, do it gently. Try not to drag the fish through the mud or sand because this can injure it and remove slime. Get the fish back in the water as fast as you can.
In a nutshell, circle hooks are good for the fish because fewer stripers are hooked in the stomach or in other vital organs, and they’re good for the fisherman because they increase hook-ups and reduce missed strikes. Good for the fish, good for the fisherman – that’s a winning combination.
Did you know? Circle hooks have been around for centuries. Archaeologists have recovered stone circle hooks that are tens of thousands of years old from the grave sites of indigenous cultures. J hooks came about relatively recently because they are easier to make. Once again, modern-day anglers are recognizing the benefits of circle hooks for both efficiency and conservation. This fishing technique, like the hooks themselves, has come full circle.
 Now for a fishing report. Some of the best rockfish of the year are being caught and released right now using jigs. My hottest lure over the past couple of weeks has been a 10-inch BKD in either white, chartreuse, or avocado. I’m still fishing the Bay Bridge area and the warm water discharges although I am just starting to get reports of fish in the rivers, in Eastern Bay, and on the Susquehanna Flats. The yellow perch run is nearly over and was pretty much a miss for Maryland this year. The white perch spawn is in stronger with good catches reported in the usual spawning areas including the Eastern Shore and Upper Bay tributaries. The herring spawn is on, but remember it’s illegal to fish with live herring now. Not much happening yet with hickory shad.
Now for a fishing report. Some of the best rockfish of the year are being caught and released right now using jigs. My hottest lure over the past couple of weeks has been a 10-inch BKD in either white, chartreuse, or avocado. I’m still fishing the Bay Bridge area and the warm water discharges although I am just starting to get reports of fish in the rivers, in Eastern Bay, and on the Susquehanna Flats. The yellow perch run is nearly over and was pretty much a miss for Maryland this year. The white perch spawn is in stronger with good catches reported in the usual spawning areas including the Eastern Shore and Upper Bay tributaries. The herring spawn is on, but remember it’s illegal to fish with live herring now. Not much happening yet with hickory shad.
I got my biggest fish of the year and I think my biggest striped bass ever this week. I didn’t measure or weigh it and, even though I have a good idea of how big it was, I won’t speculate publicly. It was a horse! Bay water temperatures are slightly below normal right now in the low to mid-40s with some warmer areas in the rivers. There are plenty of migratory fish moving north up the Bay. Believe it or not, some surface feeding fish have been reported in areas of warmer water. Good luck!
![darthsidious[1]](http://www.chesapeakelighttackle.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/darthsidious1-300x248.jpg) Every angler I know has lost the biggest fish they ever hooked. Well, at least we think we have. A fish that breaks a line or pulls a hook immediately grows twenty pounds in my mind. It’s in every fisherman’s nature to believe he or she had a shot at a new world record, but it got away. Nothing makes a fish bigger than almost getting caught. I had just that experience a few days ago – you know, a big fish, an epic battle, and a broken line – so I thought it might be interesting to take another look at some of the things we do wrong to make sure we never catch that fish of a lifetime.
Every angler I know has lost the biggest fish they ever hooked. Well, at least we think we have. A fish that breaks a line or pulls a hook immediately grows twenty pounds in my mind. It’s in every fisherman’s nature to believe he or she had a shot at a new world record, but it got away. Nothing makes a fish bigger than almost getting caught. I had just that experience a few days ago – you know, a big fish, an epic battle, and a broken line – so I thought it might be interesting to take another look at some of the things we do wrong to make sure we never catch that fish of a lifetime.
It’s big fish season on the Chesapeake Bay. The coldest months of the year are the absolute best times to catch & release striped bass. Stripers are hardier in the winter. They’re more muscular, carry more fat, and are almost guaranteed to survive when properly handled and released. Additionally, winter is a great time to fish the Bay because it’s almost free of boat traffic. Wildlife sightings are more common. Bald eagles are frequent. Sea ducks are everywhere. On cold, clear, calm days colors are more vivid, the water reflects more spectacularly, and we can see things farther away. Some days you can see for miles across the glass where unobstructed views of the horizon make it nearly impossible to tell where the water ends and the blue sky begins. It’s a fantastic time to enjoy the Chesapeake in all it’s winter splendor. It’s beautiful. So, c’mon, you wouldn’t want to spoil all that serenity with the biggest fish of your lifetime, would you? Here are some sure-fire things you can do to make sure you lose that bad boy! Read More!
 In the fifty years or so I’ve had to observe the behavior of fishermen, I’ve noticed a few trends. While collecting thoughts for my next book, I’m forming a list of traits that I think good fishermen have in common. In the book, I’ll concentrate primarily on gear and tackle but I also want to spend some time examining habits and attitudes that successful anglers share. You know, the right stuff. One penchant stands out above all the rest – good fishermen like to release fish. Not only do they like to let them go, but they look for ways to insure they survive once they swim away. Accomplished anglers find satisfaction in returning a fish to the water and they enjoy the thought that other fishermen will also have the opportunity to experience the thrill of a trophy catch.
In the fifty years or so I’ve had to observe the behavior of fishermen, I’ve noticed a few trends. While collecting thoughts for my next book, I’m forming a list of traits that I think good fishermen have in common. In the book, I’ll concentrate primarily on gear and tackle but I also want to spend some time examining habits and attitudes that successful anglers share. You know, the right stuff. One penchant stands out above all the rest – good fishermen like to release fish. Not only do they like to let them go, but they look for ways to insure they survive once they swim away. Accomplished anglers find satisfaction in returning a fish to the water and they enjoy the thought that other fishermen will also have the opportunity to experience the thrill of a trophy catch.
I love to eat fish. I just returned from a week-long fishing trip to the Abacos Islands where my sons and I ate the fish we caught every day. I don’t begrudge anyone the opportunity to eat their catch, but every angler has to release fish from time to time. Better anglers can’t possibly eat all the fish they catch, nor do they want to. I’ve written about this in the past, so instead of going into a step-by-step breakdown of best-practices, I thought I’d try to make it a little more fun by turning it into a quiz. Think you have a good handle on how to take care of the fish you plan to release? Check it out: Read More!



